What is the standard unit of current?
 |
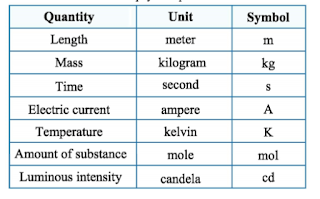
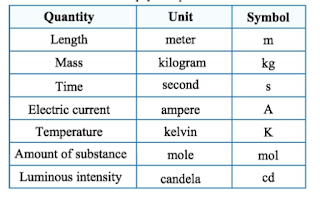
| Current |
What is the standard unit of current?
According to the
SI Unit (System International) the standard unit of current is
Ampere. Which can understand properly from the definition of current.
Definition of Current:
Current is defined as the rate at which charge passes by a point on the circuit. If we consider a small cross section of a wire that could be isolated and a quantity of
charge (Q) that passes through that cross section in a certain amount of
time (t) that could be measured, then the current would be the ratio of
"Q/t"
So the ration of charge passing and the time of charge passing is mainly the unit Ampere.
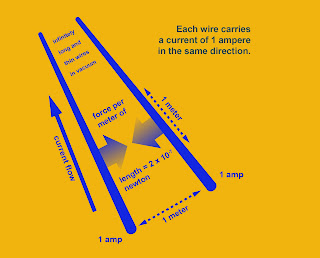 |
| Current and it's unit Ampere |
In general,
the amount of electric charge passing through a point in an electric circuit per unit time, with an equivalent charge to 6.241× 10^18 charge carriers which is (1 coulomb ) per second constructing 1 Ampere.
Current = flow of charge / per unit time = one coulomb / one second that is called or known as 1 Ampere.
Also, If we consider 2 same wires that are separated by a distance of
1 meter and a same amount of current is flowing through them, and if they experiences a force of
2×10^-7 N, then the amount of current flowing through them is called
1 Ampere.